When you get hungry, you grab
a snack from your fridge or pantry. But what can plants do when they get
hungry? You are probably aware that plants need sunlight, water, and a home
(like soil) to grow, but where do they get their food? They make it themselves!
Plants are called autotrophs
because they can use energy from light to synthesize, or make, their own food
source. Many people believe they are “feeding” a plant when they put it in
soil, water it, or place it outside in the Sun, but none of these things are
considered food.
Rather, plants use sunlight, water, and the gases in the air
to make glucose, which is a form of sugar that plants need to survive. This
process is called photosynthesis and is performed by all plants, algae, and
even some microorganisms. To perform photosynthesis, plants need three things:
carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight.
Just like you, plants need to
take in gases in order to live. Animals take in gases through a process called
respiration. During the respiration process, animals inhale all of the gases in
the atmosphere, but the only gas that is retained and not immediately exhaled
is oxygen.
Plants, however, take in and
use carbon dioxide gas for photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide enters through tiny
holes in a plant’s leaves, flowers, branches, stems, and roots. Plants also
require water to make their food.
Depending on the environment,
a plant’s access to water will vary. For example, desert plants, like a cactus,
have less available water than a lilypad in a pond, but every photosynthetic
organism has some sort of adaptation, or special structure, designed to collect
water.
For most plants, roots are responsible for absorbing water.
The last requirement for
photosynthesis is an important one because it provides the energy to make sugar.
How does a plant take carbon dioxide and water molecules and make a food
molecule? The Sun!
The energy from light causes a chemical reaction that breaks down the molecules of carbon dioxide and water and reorganizes them to make the sugar (glucose) and oxygen gas.
It would be impossible to
overestimate the importance of photosynthesis in the maintenance of life on
Earth. If photosynthesis ceased, there would soon be little food or other
organic matter on Earth. Most organisms would disappear, and in time Earth’s atmosphere
would become nearly devoid of gaseous oxygen.
Energy produced by
photosynthesis carried out by plants millions of years ago is responsible for
the fossil fuels (i.e., coal, oil, and gas) that power industrial society. In
past ages, green plants and small organisms that fed on plants increased faster
than they were consumed, and their remains were deposited in Earth’s crust by
sedimentation and other geological processes.
There, protected from oxidation,
these organic remains were slowly converted to fossil fuels. These fuels not
only provide much of the energy used in factories, homes, and transportation
but also serve as the raw material for plastics and other synthetic products.
Unfortunately, modern civilization is using up in a few centuries the excess of
photosynthetic production accumulated over millions of years. Consequently, the
carbon dioxide that has been removed from the air to make carbohydrates in
photosynthesis over millions of years is being returned at an incredibly rapid
rate. The carbon dioxide concentration in Earth’s atmosphere is rising the
fastest it ever has in Earth’s history, and this phenomenon is expected to have
major implications on Earth’s climate.
Please leave a comment! I hope you liked the post! See you soon!













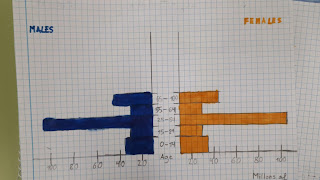
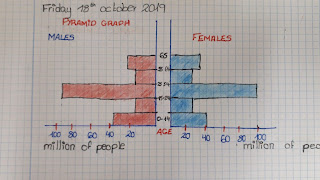














.jpg)






