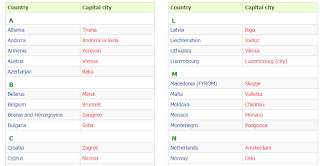
Here are all the capitals of Europe.
The blog where you will learn a lot of science, history and English by Simon Hergueta.
Friday, 4 December 2020
Tuesday, 1 December 2020
Monday, 30 November 2020
Monday, 23 November 2020
Gerunds and Infinitives
There are certain words in English that are usually followed by an infinitive or a gerund. When these words are followed by an infinitive, this could be with or without to. Gerunds are form adding -ing to the base form.
To know you is to love you.
She made her swim.
Cycling is good for your health.
Before going to bed he turned of the light.
Some verbs can be followed by a gerund or by an infinitive with no difference in meaning.
Begin, like, continue, love, hate, prefer, intend and start.
I started to read. = I started reading.
Here is a video:
Here is an advanced video, you don't need to understand all of it. It's a good listening.
The musculoskeletal System
Wednesday, 18 November 2020
European Political Map
Tuesday, 3 November 2020
Plate Tectonics Theory
The theory, or idea, of plate tectonics says that Earth’s outer layer is made up of large, moving pieces called plates.
German meteorologist Alfred Wegener is often credited as the first to develop a theory of plate tectonics, in the form of continental drift.
Bringing together a large mass of geologic and paleontological data, Wegener postulated that throughout most of geologic time there was only one continent, which he called Pangea, and the breakup of this continent heralded Earth’s current continental configuration as the continent-sized parts began to move away from one another.
Scientists discovered later that Pangea fragmented early in the Jurassic Period. Wegener presented the idea of continental drift and some of the supporting evidence in a lecture in 1912, followed by his major published work, The Origin of Continents and Oceans (1915).
All of Earth’s land and water sit on these plates. The plates are made of solid rock. Under the plates is a weaker layer of partially melted rock. The plates are constantly moving over this weaker layer.
Watch this video if you want to know more:
Enjoy!
Monday, 26 October 2020
Spanish Geography (review of all the contents)
In this post we are going to review Spanish Geography.
First of all the Spanish Relief Map.
Now you can study the Spanish Rivers. Remember that the longest river in Europe is The Volga.
Now, it's time to watch this video:
After that, take a look at your notes, play with your maps, study them... and you can go to the next part... Climates!
And finally, practice with lots of games and maps.
Don´t forget the Balearic Islands and to use good maps!
 |
| Balearic Islands |
Remember that a summit is the top of a mountain and a Peak is the pointed summit of a mountain.
Have a great day! If you miss something tell me!
Thursday, 22 October 2020
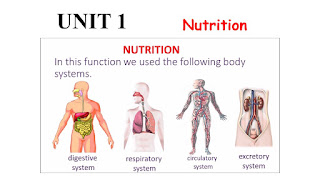
The Nutrition Function (Unit 1)
The Digestive System
The Circulatory System
Wednesday, 21 October 2020
Spanish Geography
Lost in Space S01E01
Here are the subtitles. But first let's see the Summary and the Plot.
Summary
On the way to a space colony, a crisis sends the Robinsons hurtling towards an unfamiliar planet, where they struggle to survive a harrowing night.
Plot
The Robinson family is seen playing a card game, Go Fish, when their ship crash lands on an unknown planet. They manage to evacuate the ship safely but, once they do, the ship sinks. Everyone is okay although Maureen Robinson has broken her leg. They set up camp but realize that without a power source they'll freeze. John Robinson decides that someone needs to swim down to the ship and retrieve a battery. He suggests that Will Robinson go but Judy Robinson beats him to it. She manages to get a chariot battery but as she starts to swim back up the water begins to freeze around her. She manages to escape the ship but ends up getting stuck just below the surface. They try to use a pick to get her out but the ice is too thick.
Will looks up and sees white flames and identifies them as magnesium. John and Will set out to get some to bring back. While they're away, Penny Robinson reads to Judy and Judy helps Penny through a medical procedure she has to do in order to save Maureen's leg. In a flashback, we learn that Maureen traded something so that Will would be approved for the trip. John and Will climb the glacier and find a cave where they are able to harvest some magnesium. Suddenly, the cave shakes and the ledge breaks off causing Will to fall into the crevice. He falls to the bottom of the glacier where he finds a forest filled with alien vegetation. John makes the hard choice and leaves Will behind to go help Judy. Meanwhile, Will goes exploring. He finds an alien ship and runs into an extraterrestrial. Well, the bottom half of one. It gives chase as Will climbs a tree unbeknownst to him that the alien's top half is stuck in the same tree.
John returns to camp with the magnesium. He uses it to burn a hole in the ice. In a flashback, we learn that John and Maureen are separated and that Maureen needs John's permission to take the kids on the trip. Will makes conversation with the alien and learns that he's new to this planet as well. While the magnesium works, it suddenly starts to rain frustrating their efforts to save Judy. She starts to freak out because she thinks that she's going to die today. The forest Will's in catches fire and traps Will up in the tree. He sacrifices himself and uses his tools to free the alien so at least it can survive. Because of this act of kindness, the alien comes back and rescues Will from the fire.
Everyone is holding Judy's hand as she slowly dies. That's when the alien arrives with Will in tow. Will asks the alien if he can do anything to help. It uses its hands to heat up the ice and reaches down to fish out Judy. The family rejoices and huddle around Judy to keep warm. Will asks the alien if there's anything he can do to keep them warm. The alien lifts its hands and uses the heat emitting from them to keep the Robinsons warm.
In a flashback, we learn that the Resolute was attacked by the alien creature which caused the humans to abandon ship. A woman is hiding from the robot when a man falls next to her having been shot. She pretends to take care of him but steals his jacket and his identity and becomes "Dr. Smith." She commandeers a ship and brings along two mechanics desperate to get off the ship as well.
Subtitles
If you want to download the file with the subtitles just clic on the image below.
Here are the first lines anyway:
Four, four.
Okay. Everyone remember the rules?
Are you sure this is the best idea?
What else are we gonna do?
- Okay, have you got any eights?
- Uh...
Go fish.
Hey, it's your turn.
Uh, um...
Go fish.
The Resolute made 23 routine trips.
So what happened to ours?
There's no use in speculating.
Completing de-orbit burn.
Helmets on.
Begin entry phase in 30 seconds.</i>
Okay. Um, it's still my turn.
Do you have any nines?
- Seriously, Penny?
- What?
Did you see my hand?
You count cards.
I don't know why everyone doesn't.
Okay, can I have my nine, please?
Friday, 16 October 2020
Dictation #2
Correct your dictation and tell me how many mistakes you have. If you make a spelling mistake in one word, a good trick or advice is to write that word again five times focusing on the spelling.
Then next day try to write it again without looking.
Was it easy?
Spanish Climates: Oceanic, Mediterranean, Mountain Climate, Continental and Tropical
Oceanic climate
Also called coastal or maritime.
Temperature: mild winters and summers. Winters are cool but not very cold. Not big changes in temperature.
Precipitation: constant throughout the year, although there is less summer. There’s no dry season. Lots of clouds.
Where? West of Europe. In Spain in the Cantabrian Watershed.
 |
| Oceanic Climate |
Vegetation: deciduous trees, like oak, beech, eucalyptus. On the coast there are flat areas of wild plants, shrubs, grass and bushes.
Landscape: humid regions with a great deal of vegetation due to abundant rainfalls and rich soil. Extensive forests of deciduous trees such as oaks and beeches with bushes and grassy meadows for livestock.
Mediterranean climate
Temperature: Mild. Few extreme temperatures. The average is around 15°C. But normally the temperature is over 22°C.
Only two seasons: summer and winter. Summers are longer than winter and the winter is very mild. Eastern and southern Spain as well as the Balearic Islands.
Vegetation: Dehesa forests of evergreen species such as holm oaks, cork oaks, and pines, with two kinds of bushes:
- Maquis Shrubland: very dense and compact with tall bushes such as the strawberry tree, heather and the rockrose.
- Thickets: low bushes found in drier areas such as rosemary, thyme and lavender.
 |
| Mediterranean Climate |
Mountain Climate
Where? Peaks higher than 2.000 meters more or less. Examples: Navacerrada, Potes, Sistema Central, Sistemas Béticos, Pyrenees. Sierra de Guadarrama. Sierra de Gredos.
Extensive forests of evergreen trees such as pine woods or deciduous trees such as beech woods. In the summits, if it’s very high, there are no trees.
Low temperatures. Snow in winter. High range of changes. Weather conditions can change very quickly with strong winds, storms, rainfalls, snow, hail or fog.
Always take precautions if you go out hiking.
Parts of a mountain: foot, slope, peak and summit.
 |
| Mountain Climate |
 |
| Continental Climate (Meseta Central) |
 |
| La Palma (Tropical Climate) |
Wednesday, 14 October 2020
Excretory System
The excretory system consists of the urinary system and the sweat glands.
The urinary system
The urinary system is formed by the kidneys, the ureters, tha bladder and the urethra. The filtered waste substances in the kidneys are mixed with water to make urine. This leaves the kidneys through the ureters and accumulates in the bladder. When the bladder is full, urine is expelled from the body through the urethra.
Do you want to know more about waht water does in our body? Check this link to find out water journey in the body. It's very interesting!
Kidneys
They filter the blood and also clean it.
Sweat glands
We sweat when we do exercise or sports, when it is hot and also when we get nervous. Sweat is a mixture of water and waste substances. But it has also many more things.
What your sweat is composed of depends on which gland the sweat is coming out of. There are many different types of glands on the human body, but generally, only two main ones are recognized:
Eccrine glands produce most of your sweat, especially the watery kind. But eccrine perspiration doesn’t taste like water, because bits of salt, protein, urea, and ammonia gets mixed into it. These glands are mostly concentrated on the palms, soles (plantas de los pies), forehead, and armpit, but cover your entire body.
Apocrine glands are larger. They’re mostly located on the armpits (axilas), groin (ingle), and breast area. They’re the ones most often associated with BO and produce more concentrated secretions after puberty. Since they’re near hair follicles, they typically smell the worst. This is why people often say stress sweat smells worse than other types of sweat.
The functions of sweat glands are the following:
- To filter the blood.
- To control body temperature.
Tuesday, 29 September 2020
Spanish Rivers
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river.
Parts of a river
Source: where a river begins.
Falls: a steep descent of the water of a river.
Flood: the rising of a river and its overflowing onto normally dry land.
Tributary: a branch that flows into the main stream.
Gravity: force that causes water to flow in a certain direction.
Dam: a barrier constructed to contain the flow of water. Normally it has a power station.
Reservoir: a lake in a river produced by a dam.
Cantabrian watershed: rivers are close to the coast. They are short and fast flowing. There is a lot of rain. They have permanent flow. Bidasoa, Nervión, Ibaizábal, Asón, Miera, Pas, Saja, Nansa, Deva Sella, Nalón, Navia and Eo.
Atlantic watershed: here we have rivers that flow into the Atlantic Sea. There are two types:
a) Galician’s coast. They have an abundant flow. They are long because the mountains are far away from the coast. Miño, Tambre and Ulla.
b) Rivers from the Central Plateau: these are the longest in Spain. Their source is in the mountains close to the mediterranean. They have irregular flow. Duero, Tajo, Guadiana and Guadalquivir.
Main rivers
The most important rivers in Spain are the following (from north to south and from west to east): Miño, Duero, Tajo, Guadiana, Guadalquivir, Júcar and Ebro.
Miño: It has a lenght of 310 km. It goes through Lugo, Orense, Pontevedra and Portugal. Its main tributary is river Sil.
Duero: Its source is in Urbion peaks. The third longest rivers in Spain and peninsula. Length of 897 km. Its mouth is in Oporto. Its tributaries with more than 100 km are: Águeda, Zapardiel, Duratón, Adaja, Tormes, Valderauey, Pisuerga Esla and Huebra.
Tajo: the source is in the Universal mountains and goes along Teruel, Cuenca, Guadalajara, Madrid, Toledo, Cáceres and Portugal. It is the longest river in the peninsula (but not in Spain) with a length of 1088 km. Its mouth is in Lisbon.
Guadiana: Its source is in Ojos de Guadiana. It has 744 km. It goes across the south plateau. Its length is 818 km. It goes along Albacete, Ciudad Real, Badajoz and Huelva.
Guadalquivir: Its source is in Cañada de las Fuentes and its mouth is in Sanlúcar de Barrameda. Its length is 657 km. It’s the fifth river. It goes along Jaén, Córdoba, Sevilla, Huelva and Cádiz.
Júcar: It has 497 km of length. It goes along Cuenca, Albacete and Valencia.
Ebro: Its source is in Cantabria in Fontibre and it flows into the mediterranean in Tarragona. Length: 930 km. It is the longest in Spain. It goes along Cantabria, Palencia, Burgos, La Rioja, Álava, Navarra, Zaragoza and Tarragona.
Other rivers in the world:
Amazon: the largest river in South America 6992 km. Nile: The largest river in Africa. 6853 km
Volga: the largest river in Europe. 3692 km.
Now you can watch this video that includes everything: